Female abdominal hernia symptoms can vary from woman to woman. In general the disease is more common in men – however it can also affect women! Treatment is necessary if the symptoms are bothering you a lot. Though in most cases the disease is not immediately life-threatening, it’s important to understand when to seek immediate medical help since there is a chance for the problem to turn into serious.
What actually is abdominal hernia?
A hernia is a condition in which you have the protrusion of tissue or organ of the body from its naturally contained space. Typically it occurs in the abdomen, groin and upper thigh areas – though in a few cases it may occur elsewhere in the body.
Abdominal hernia usually involves a part of bowel (intestine, colon, and rectum) or omentum (a fatty, membranous double layer that hangs down from the stomach to help cover and support many organs in the abdominal area). It can protrude through an opening or weak area in your abdominal wall.
Weak spots in the abdominal wall can develop with several ways. They may develop with age (acquired), or some may be present at birth.
Certain people get abdominal hernias with a congenital defect (born with abnormal thin of abdominal wall). In other cases, the problem develops with the following ways:
- The strength of abdominal wall weakens gradually due to years of absorbing stress. This can occur as you age.
- In women, the risk of developing the problem increases during or after pregnancy.
- After an abdominal surgery. Having a surgery in your abdominal area can increase the risk of hernia months or years afterward.
Other risk factors include having injuries in the abdominal area, a personal history of hernia, a family history of hernia, obesity, poor diet (especially low in fiber that makes you need extra straining during bowel movement), and frequently pushing /lifting heavy objects.
Abdominal hernias, especially ventral hernias, often require surgical operation (they usually don’t heal without treatment). Non-surgical procedures can also help improve the symptoms, but they don’t repair the hernia.
So surgery is the main treatment option. It can help repair the hernia and reduce the risk of hernia strangulation (a serious complication of the disease that can cut off the blood flow to the affected area).
According to the Journal of American surgery; surgery is usually required when ventral hernia becomes massive, it has at least 15 cm (length) or 150 cm2 (width). The risk of having recurrence increases as the problem grows in size. For more guidance, ask a doctor!
Female abdominal hernia symptoms
Since some types of abdominal hernias can turn into serious, immediate treatment may be necessary. Early diagnosis is required so your doctor can treat the problem appropriately and prevent serious complications of the disease.
The disease can cause an array of symptoms
In the early stages of the disease, you may have no any symptom. The symptoms, especially the bulge, may take weeks or months to appear. Also, the symptoms are sometimes dependent on where the hernia appears. The bulge can appear anywhere in the abdominal wall.
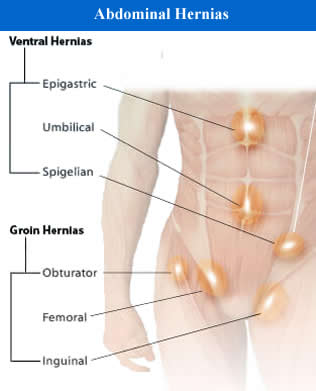
Abdominal hernia is usually named after the specific location where it occurs. For example, if it occurs in the upper thigh, it’s called femoral hernia.
How the bulge looks like may vary. But many times it feels like a round lump. And though it usually develops gradually that take weeks or even months to appear, sometimes it may occur all of a sudden after lifting heavy objects, extreme laughing, very deep coughing, intense straining or bending (especially if you have had a recent abdominal surgery).
The bulge can be painful or more sensitive to touch, though sometimes the disease can also cause a painless bulge until it gets larger. Depending on where the bulge occurs and the severity of the disease, you may find that the bulge looks smaller or even disappears when you lie down.
On the other hand, the bulge usually enlarges with standing, bending, coughing, lifting heavy weights, or when you put pressure on the affected area. You may also have other discomforts in the area of the hernia such as a feeling of burning, heaviness, or tugging. Sometimes swelling occurs, too.
The hernia pain can get worse when the contents of hernia become stuck /trapped, typically characterized by difficulty in pushing the bulge back in (more difficult to be manipulated both spontaneously and manually). This is called ‘incarcerated hernia’.
But many times, abdominal hernias in women are not easy to diagnose. They’re relatively smaller and more difficult to discover (hidden inside). As a result, they may not cause an obvious lump, making the diagnosis need some careful medical sleuthing – read more! If you in-doubt to any symptom you’re experiencing, see your doctor for accurate diagnosis.
Here are other tips that may help identify the problem: