As the name suggests, sinusitis headache a.k.a sinus headache is a consequence of inflamed sinuses (sinusitis). How does it feel like? This may vary from person to person. But in general, this uncommon type of headache is felt as a constant dull, throbbing pain over the affected sinus (typically in the upper face such as the forehead, cheeks, or around the eyes). Does it also spread to the back of head?
What actually is sinusitis?
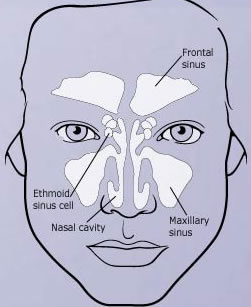
It is an inflammation of the tissue lining you sinuses located behind the trestle of your nose, inside your cheekbones, and forehead – see the following image, credit to WebMD.
Sinuses are normally filled with air, that’s why they are also often called as air-filled cavities. In sinusitis, the sinus’s lining tissue gets inflamed and swollen, blocking the flow of mucus that normally drains into the nose. As a result, there will be bacteria, fungi, or viruses that can overgrow and cause an infection, worsening the problem.
This blockage can be triggered by a number of causes, such as allergic reaction, common cold, or particular disorders (like deviated septum and nasal polyps). People with a condition that weakens their body immune system are also at high risk. If the immune system is not as strong as usual, the infection is relatively easier to develop.
There are several different types of sinusitis. These include:
- Acute sinusitis, typically characterized by cold-like symptoms such as nasal symptoms (blocked or runny nose) and facial pain. It usually lasts less than 4 weeks.
- Sub-acute, if the problem lasts about 4-8 weeks.
- Chronic, if it lasts 8 weeks or more.
- And recurrent sinusitis. It is a term used if the problem attacks several times a year.
Fortunately, it is usually harmless and the treatment is not always necessary. Even many times, it responds to lifestyle measures (taking rest and keeping hydrated are often enough to help cope with).
Migraine and tension-type headaches
It is not easy to distinguish between sinus headache and other types of headaches (particularly such as migraine and tension headaches).
In fact, the symptoms of these types of headaches often overlap! For example, migraine and sinus headache can worsen when you bend forward.
Migraine
It can be a mild or severe headache (throbbing pain), typically occurs on one side of the head. Sometimes, it may be followed with other symptoms such as more sensitive to sound /light, nausea, and vomiting.
The cause of migraine is not fully known, but it is often associated with the consequence of temporary changes in particular nerves or chemicals in the brain. People with the following risk factors are more vulnerable to have migraine:
- Having a close relative with the same problem. About 50 percent of people with migraine have a family history with the condition. This may suggests that genes may have an effect.
- In some cases, migraine is linked to particular triggers such as tiredness, stress, or during menstrual period (in women of childbearing age).
Sometimes it may be linked to particular underlying condition. You should seek help promptly if you also experience:
- Weakness (paralysis) in one /both sides of the face or arms.
- Garbled, slurred speech.
- Or other serious symptoms such as mental confusion, stiff neck, and seizures.
Tension-type headaches
It may be the most common type of headache, and anyone can have it at some point in life. Most of the time, it is harmless (not serious) and has nothing to do with another underlying cause. Even it is the one we usually think of as a normal.
How does it feel like? In tension-type headache, a constant ache affects both sides of your head. It may be followed with other symptoms such as pressure behind the eyes or/and increased tightness of muscles in the neck.
But again in general, it is usually mild and will not severe enough to interfere with your daily activities. It will relieve within a few days – though it can last 30 minutes or even a few hours.
Like in migraine, the exact cause of tension-type headaches is also not clearly understood yet.
But there are certain factors /conditions that may trigger them, these include; dehydration, tiredness, squinting, missing meals, stress, anxiety, particular smells, extreme noise, extreme light (such as very bright sunlight), lack of exercise (physical activity), or poor posture.
Sinusitis headache
The inflammation and infection in sinusitis may cause pain or pressure over the affected sinus, causing headache. You may feel it around your eyes, forehead, or cheeks – again, depending on where the inflammation occurs.
Typically, sinus headache occurs only on one side. It may worsen when you lie down or bend forward. Exposure to extreme temperature (such as moving from a warm air ‘indoor’ into freezing air ‘outside’) may make it get worse, too. Furthermore, it often flares up in the morning and may slightly get better by the afternoon.
Another thing you need to know, headache associated with sinusitis is usually followed with other symptoms of sinusitis – particularly such as:
- Stuffy or runny nose (nasal symptoms). You may also have yellow or green mucus discharge.
- The face may become more sensitive, it may feel tender and swollen to touch.
- A high temperature (fever).
- Fatigue or tiredness.
- Achy feeling in your teeth (particularly upper teeth).
Can sinusitis lead to headache in the back of head?